Markus Holling is a board-certified neurosurgeon, deputy chairman of the department of neurosurgery and head of the vascular section, University Hospital Münster, Germany. Besides his work at the department of neurosurgery, he is a board-certified Emergency Physician and has a passion for teaching, being several times awarded as teacher of the year. Dr. Markus Holling is married and father of two sons.
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Münster University Hospital (UKM) is a German maximum-care hospital in Münster. It has 1,513 beds in which a total of 55,582 inpatients and 499,113 outpatients were treated in 2020. It consists of over 40 individual clinics and polyclinics that work closely with the Medical Faculty of the Westphalian Wilhelms University of Münster.
Three-Dimensional VR Anatomy
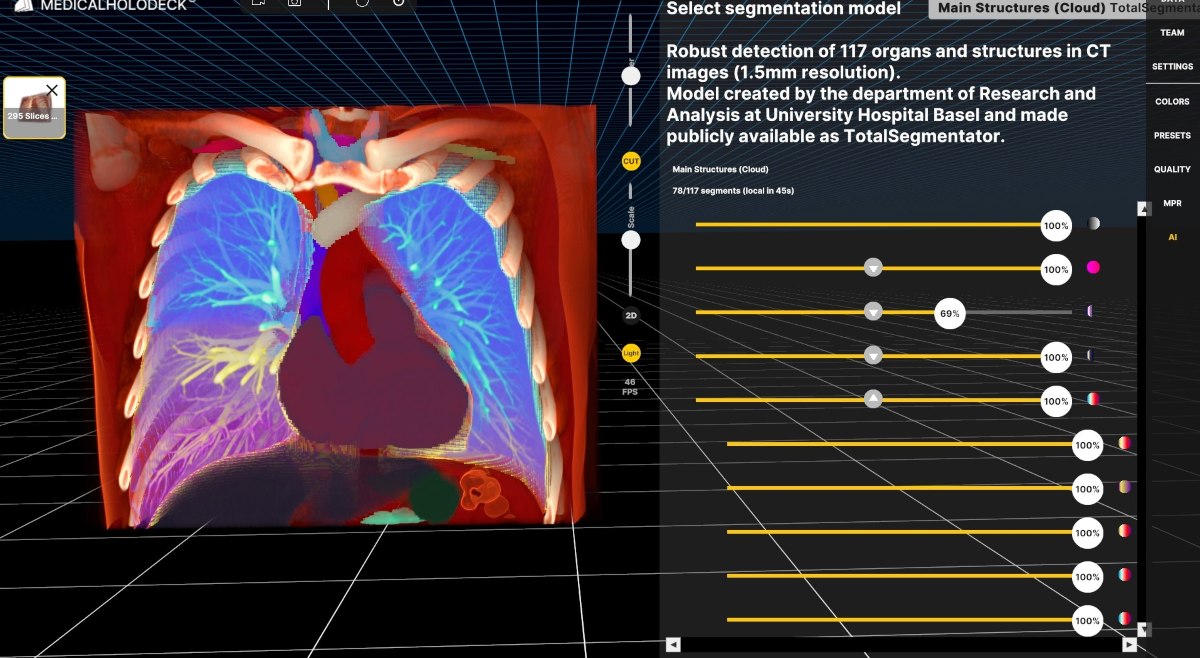
At the core of Anatomy Master 2 lies its three-dimensional representation of human anatomy, offering an unparalleled tool for both learning and teaching. The VR environment provides an immersive experience that allows users to explore over 2000 precisely crafted anatomical structures and organs as if they were walking around and dissecting them in real space.
Why did you choose Medicalholodeck? Which needs does it fulfill?
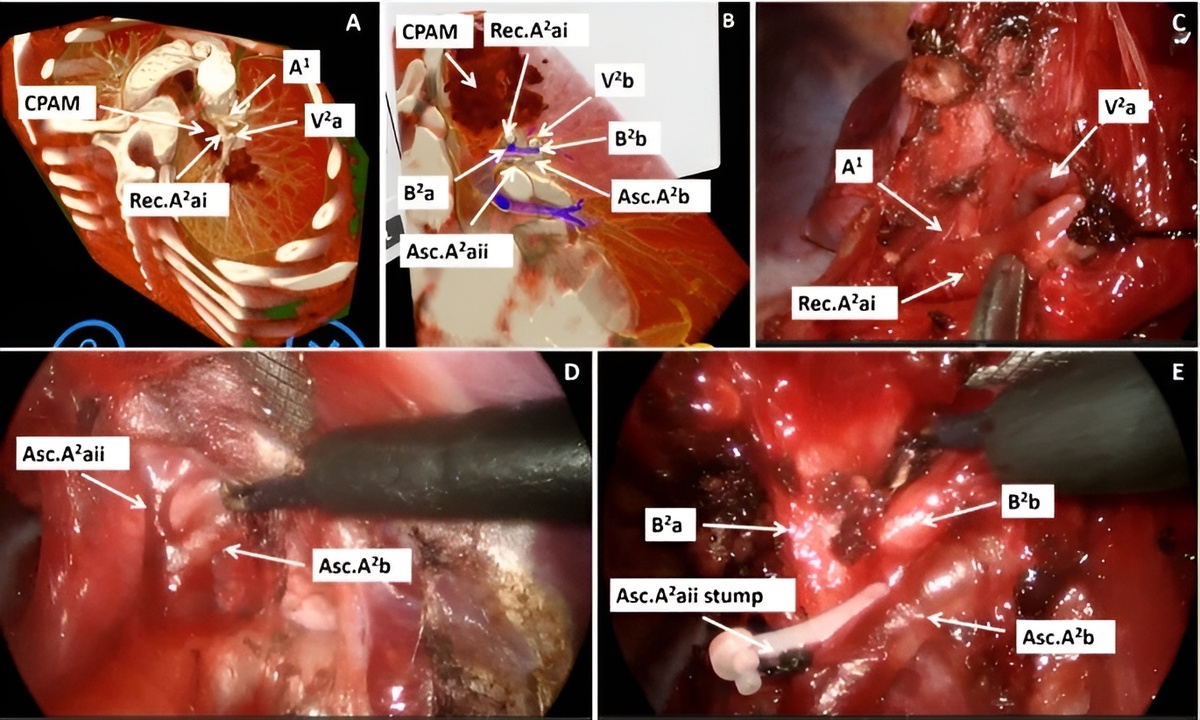
In medical training, the patient-specific representation of anatomical conditions plays an increasingly important role. Neuroanatomy is so complex that knowledge must not only be constantly refreshed, but one must also take into account the peculiarities of each patient. In neurosurgery, there is a lot of anatomy in a very small space, so the adequate interpretation of the structures during surgery is indispensable and crucial for success.
Additionally, there is the adequate recognition of pathologies and the differentiation from a healthy environment - both on preoperative imaging and during surgery. This distinction is particularly difficult and requires constant practice and training. Neurosurgery requires first-class and patient-specifically medical visualization. This can be used in student teaching and in the further training of residents.
Background
Experience over the past decade has shown that computationally demanding 3-D imaging is increasingly available due to rapid technological advances. Applied in thoracic imaging, it simplifies the understanding of the anatomy for both the trainee and the experienced surgeon and can increase the operational and technical quality in terms of precision, safety and speed.
What is particularly unique and game-changing about the features and benefits of Medicalholodeck?
Well-known are software solutions for the representation of normal anatomy. Already, in medical school, one practices and learns from models. This is useful initially but quickly loses value due to the limited number of real-life patient cases.
Software solutions like Medicalholodeck can solve this problem. Patient-specific representations can easily be created using actual patient data, and these digital twins can be viewed and modified by all participants in real-time. This trains the recognition of healthy anatomy as well as the recognition of normal variants up to pathologies.
Which Technology do you use in Münster?
In 2019, we used Medicalholodeck on PC VR in a tethered virtual reality setup with standard Nvidia gaming GPUs. In the meantime, we installed our own on-premise GPU cloud on-site, using RTX A 6000 GPUs. We then connect with the lightweight Oculus Quest 2 using the Nvidia CloudXR SDK. This setup also allows us to use the Medicalholodeck location independently. The students can now connect to Medicalholodeck from anywhere in the hospital.
What goals are met with Medicalholodeck and virtual reality?
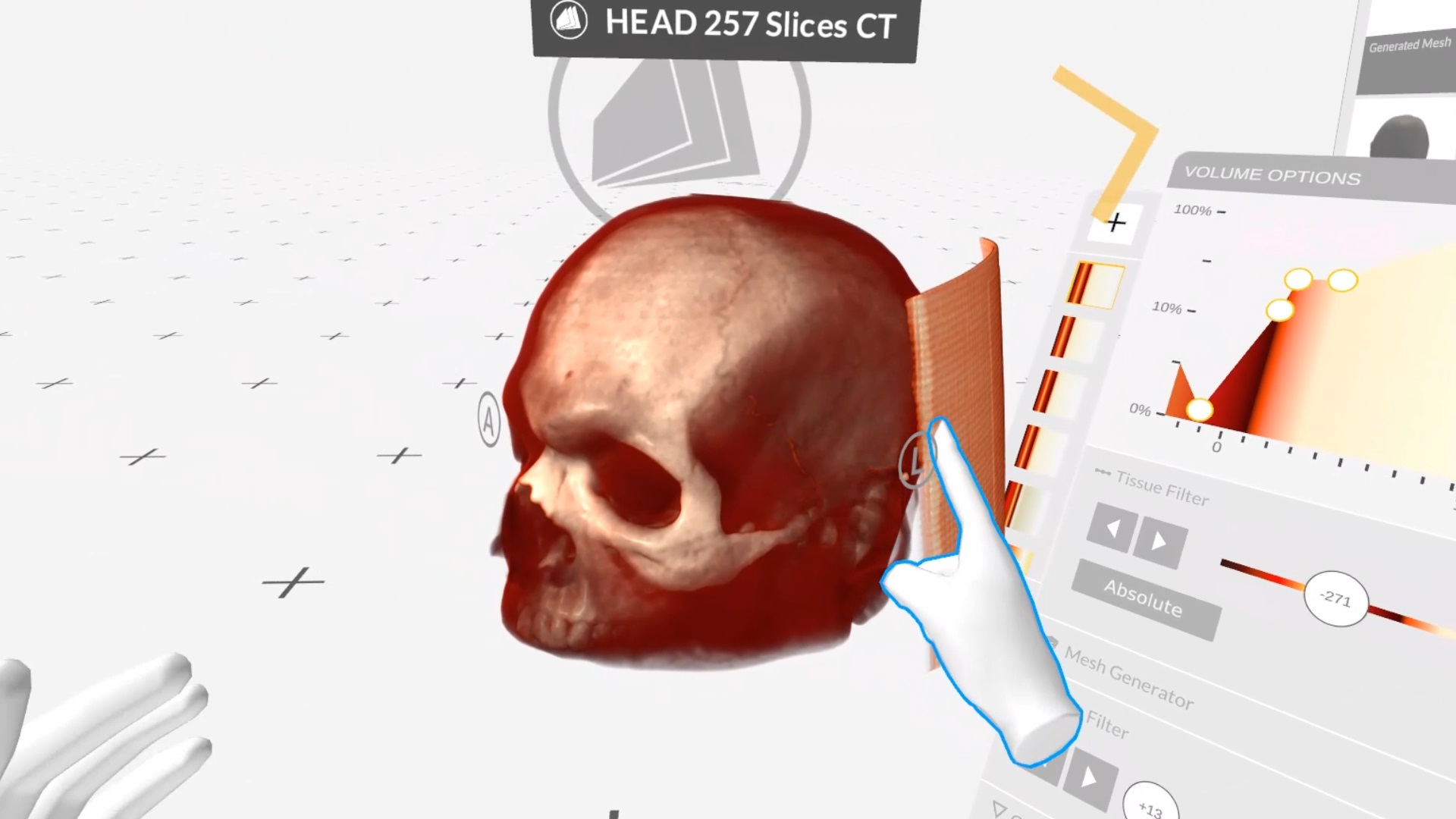
In our case, the biggest challenge for neurosurgery students is the transformation of two-dimensional, black and white sectional images from CT and MRI machines into three-dimensional bodies - skulls. Correctly interpreting these 2D images into a three-dimensional head requires much experience.
Teaching in virtual reality skips the interpretation step from 2D to 3D and allows students to work directly and immediately on three-dimensional patient data. As a result, they understand the anatomy and complex relationships better and faster and can immediately focus on the medical problem and the neurosurgical treatment.
Why is Remote Rendering important in medical education?
Remote Rendering combined with lightweight and inexpensive VR hardware, such as the Oculus Quest 2, brings a whole range of advantages to medical education: Teaching is no longer tied to a specific location and can be carried out flexibly anywhere at any time. This addresses the two known disadvantages: the high cost of PC power and the fixed location. The ease of use and the associated flexibility are precious in teaching.
Teaching in virtual reality skips the interpretation step from 2D to 3D and allows students to work directly and immediately on three-dimensional patient data. As a result, they understand the anatomy and complex relationships better and faster and can immediately focus on the medical problem and the neurosurgical treatment.
For more information, contact info@medicalholodeck.com May 2021