Case studies in spatial surgical planning
Precision surgery planning in pediatrics
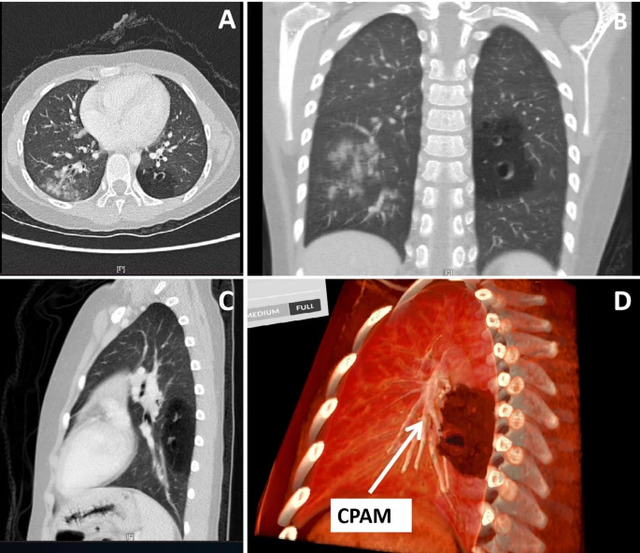
Yang W, Xu Y, Wang Z, Ye M, Chen R, Da M, Qi J (2025) Virtual reality-assisted preoperative planning for pediatric thoracoscopic segmentectomy: a retrospective study. BMC Pediatrics.
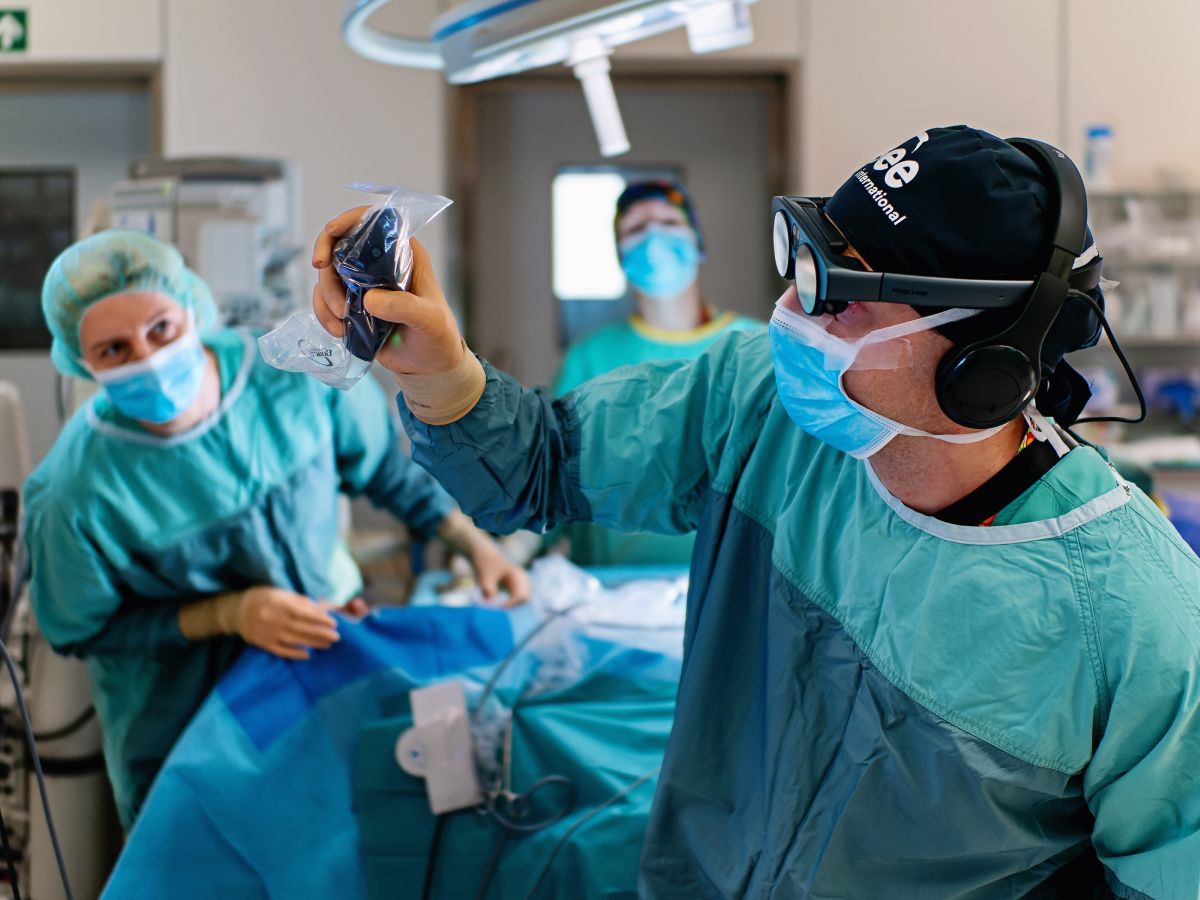
The report describes how pediatric surgeons used Medicalholodeck’s virtual reality medical imaging to support preoperative planning for thoracoscopic lung surgery in children with congenital lung malformations. By transforming CT scans into interactive, patient-specific 3D VR models, surgeons were able to better understand the spatial relationships between lung segments, lesions, and critical vessels than with conventional 2D or standard 3D imaging.
These immersive models were used to plan surgical approaches in advance and to discuss cases within the surgical team. In a series of pediatric thoracoscopic segmentectomies, the VR-based planning helped surgeons navigate complex anatomy more confidently, avoid damage to vital structures, and complete all procedures without conversion to open surgery. Independent senior surgeons confirmed that the VR models provided clearer anatomical insight than traditional imaging alone.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-025-06259-3
Spatial navigation in mandibular reconstruction
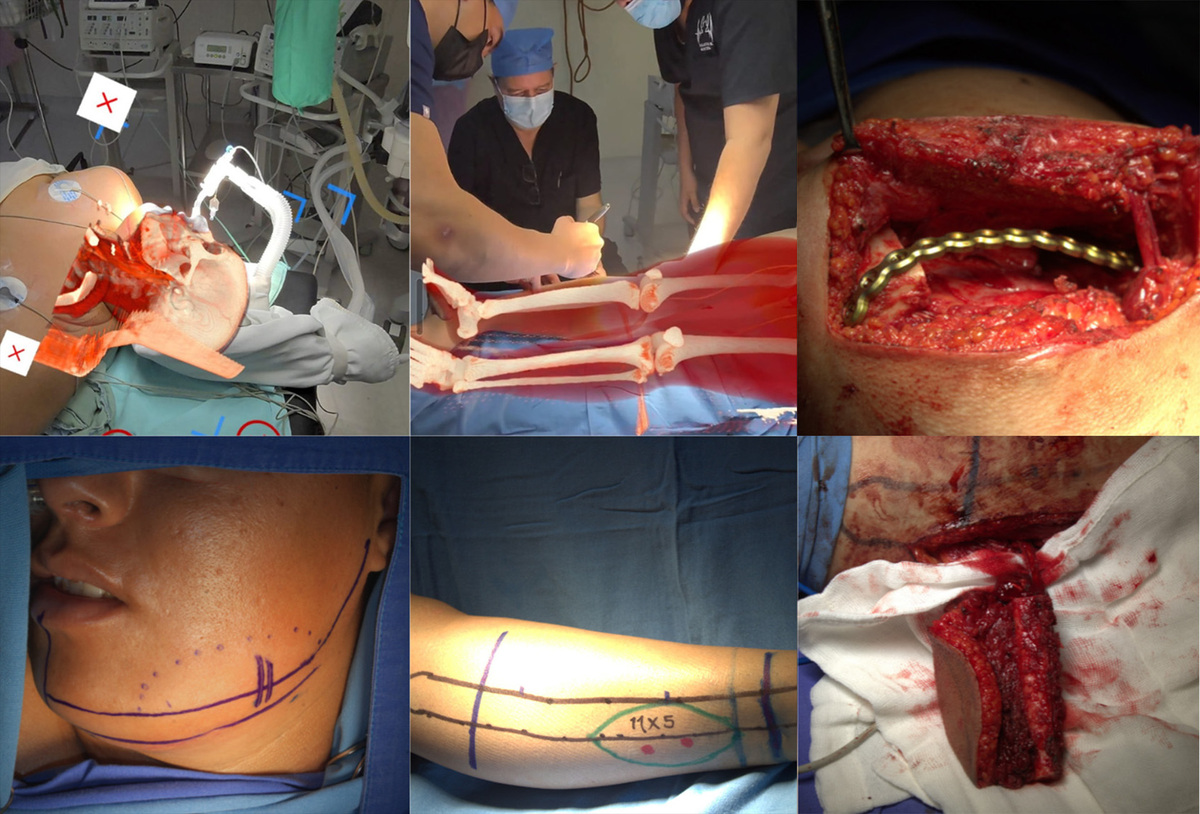
3D holographic navigation for mandibular reconstruction with a free fibula flap. CT-based holograms are overlaid in real time to guide preoperative marking, vascular planning, and microsurgical preparation of donor and recipient vessels.
Mandibular reconstruction using a fibula free flap relies on precise vascular identification, which is technically demanding even with virtual surgical planning. This report describes the first case in Latin America using a low-cost, commercially available augmented reality holographic navigation system to support complex microsurgical reconstruction.
A 26-year-old patient with a large mandibular osteoblastoma underwent preoperative planning using CT-based DICOM data to create 3D holographic models. During surgery, the AR system overlaid these models onto the operative field, enabling real-time identification of displaced recipient vessels in the neck and perforating vessels in the fibula.
An osteofascial fibula free flap was successfully harvested and transferred. The case demonstrates the feasibility and clinical value of affordable, consumer-grade holographic navigation for mandibular reconstruction.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202508.0103.v1
Orthopedic implant procedures in VR
Virtual reality enables immersive 3D visualization of patient-specific CT data, allowing surgeons to interact with both anatomy and orthopedic implants in a shared virtual environment. Unlike conventional displays, VR provides true depth perception and spatial interaction, enhancing anatomical understanding and implant planning accuracy.
Medicalholodeck, tested by NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde and NHS Lanarkshire demonstrated proof of concept for preoperative trauma planning using routine imaging and implant files. Using VR hardware and spatial imaging software, the system supports surgical planning and execution, showing high potential to improve fracture comprehension and surgical precision.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.91198
Spatial telemedicine
XR- and AI-enhanced 3D imaging enable surgeons to collaborate globally in real time. In a study conducted between Uganda and Germany, 3D patient models were created from smartphone photographs and reviewed collaboratively by surgeons in both countries using VR headsets.
The approach was fast, resource-efficient, and allowed precise planning of reconstructive surgeries. It demonstrates how specialists from other countries can provide expert guidance and support to surgeons, even across great distances, improving surgical care and training settings.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.2196/69300
Spatial imaging in spinal surgery
The benefits of virtual reality for surgical planning have been confirmed in multiple studies and real-world cases. This publication presents a 79-year-old patient with thoracic myelopathy and pseudoarthrosis who underwent a two-stage spinal revision.
The procedure was planned using spatial computing in an interactive virtual reality environment, enabling precise optimization of graft size and trajectory. The successful outcome illustrates how immersive 3D planning enhances surgical precision and supports individualized strategies in complex spine surgery.