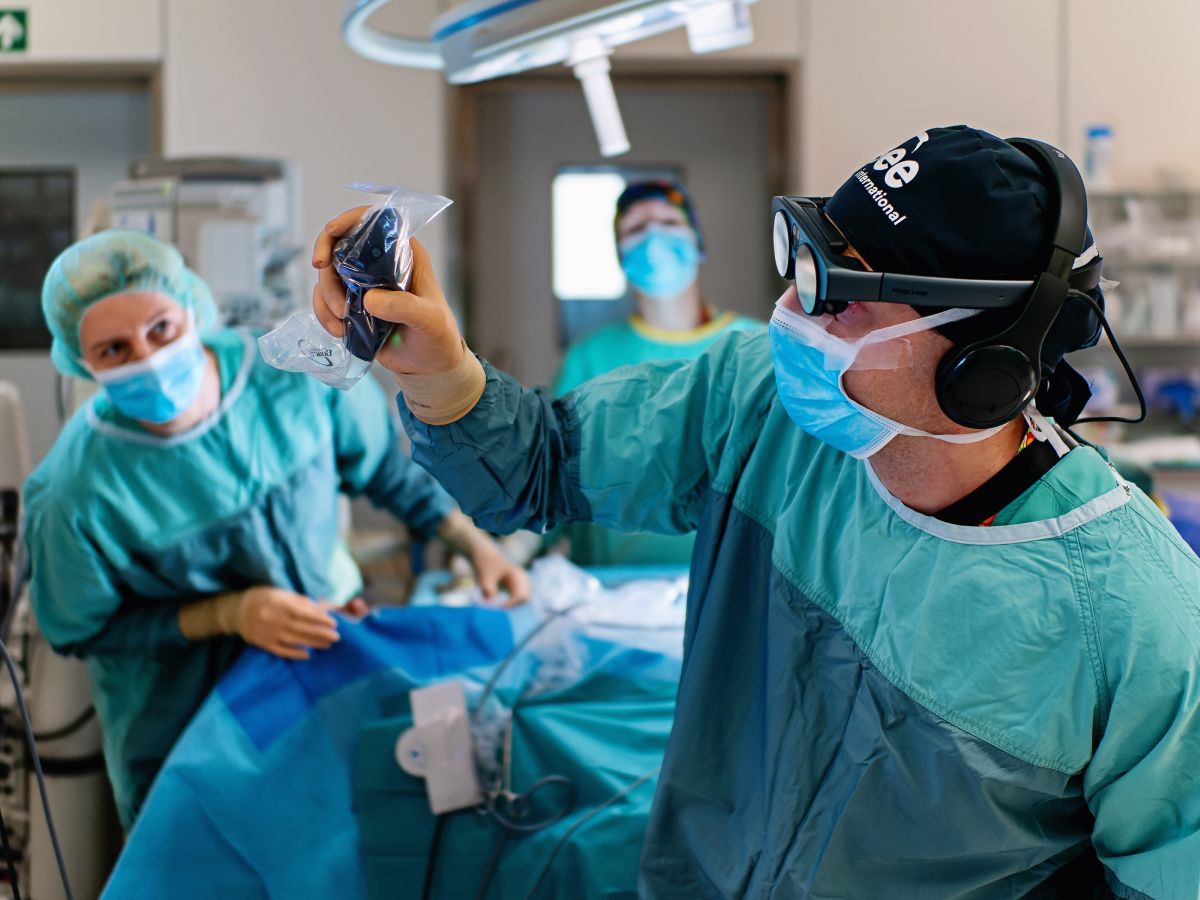
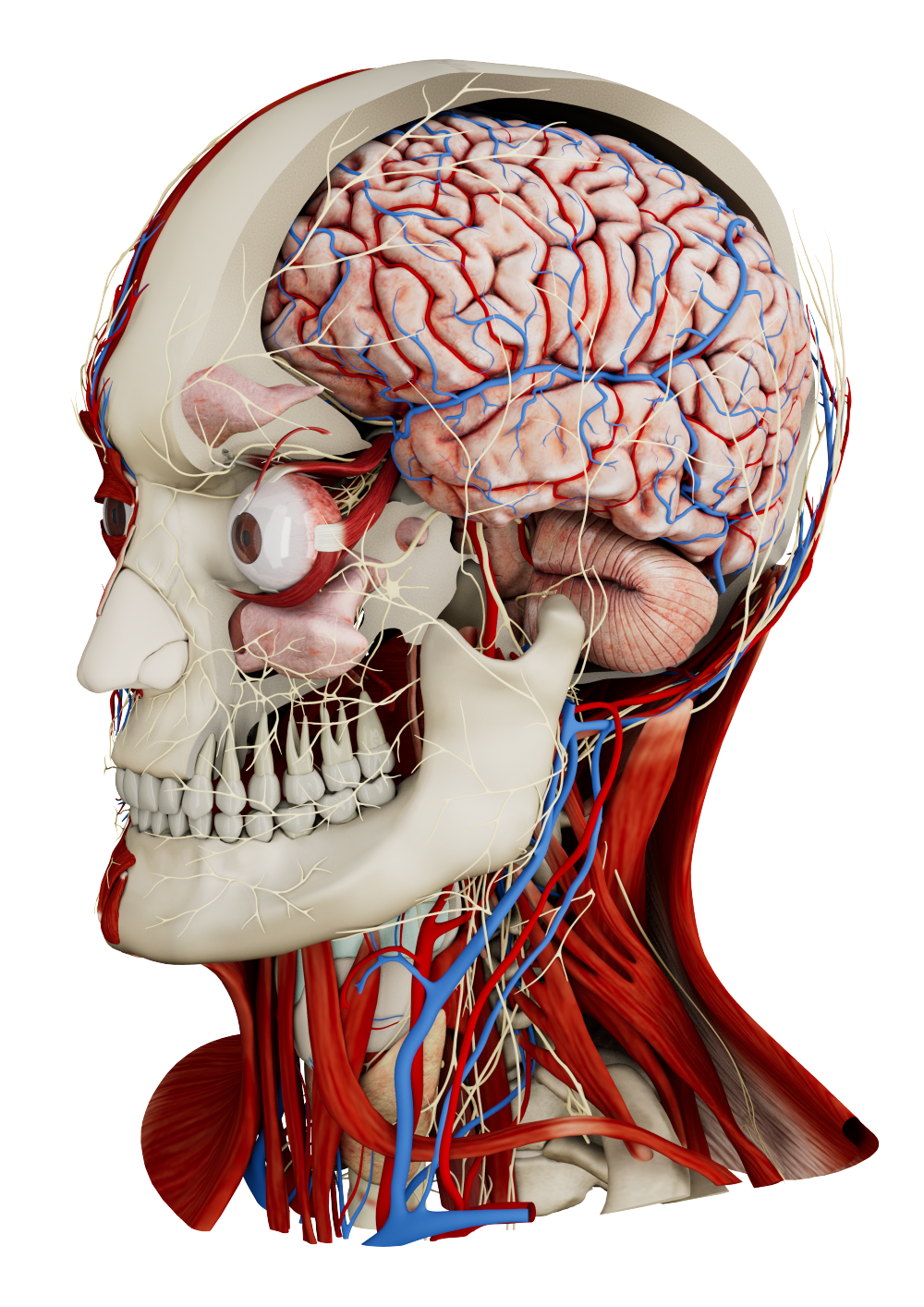
Spatial imaging and virtual reality enables cardiologists to convert 2D imaging from CT, MRI, or echocardiography into interactive 3D models. This allows for precise visualization of cardiac anatomy, supports preoperative planning for interventions, facilitates clinician training, and improves patient comprehension of complex cardiovascular conditions.
Important notice regarding surgical planning and professional clinical use
Specialized functionalities for surgical planning and pre-operative professional applications are exclusive to Medical Imaging XR PRO FDA. This version is not yet available. Information about the release date will be published here soon.
Medicalholodeck is currently undergoing the required FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and CE (Conformité Européenne) certification processes. Our team is working diligently to ensure full compliance with all regulatory standards, and we expect Medical Imaging XR PRO to be available in both the United States and the European Union soon.
For updates on product releases, regulatory progress, and availability, or for any related inquiries, please contact info@medicalholodeck.com.
Interactive cardiac anatomy
Spatial imaging and VR converts echocardiography, CT, and MRI data into fully interactive 3D models of the heart and blood vessels. Clinicians can examine chambers, valves, and coronary arteries from any angle, improving spatial awareness and interpretation of intricate anatomy that is difficult to assess on flat screens. This immersive environment also supports learning cardiac anatomy, allowing trainees and students to explore structures in detail and develop a deeper understanding of complex spatial relationships.
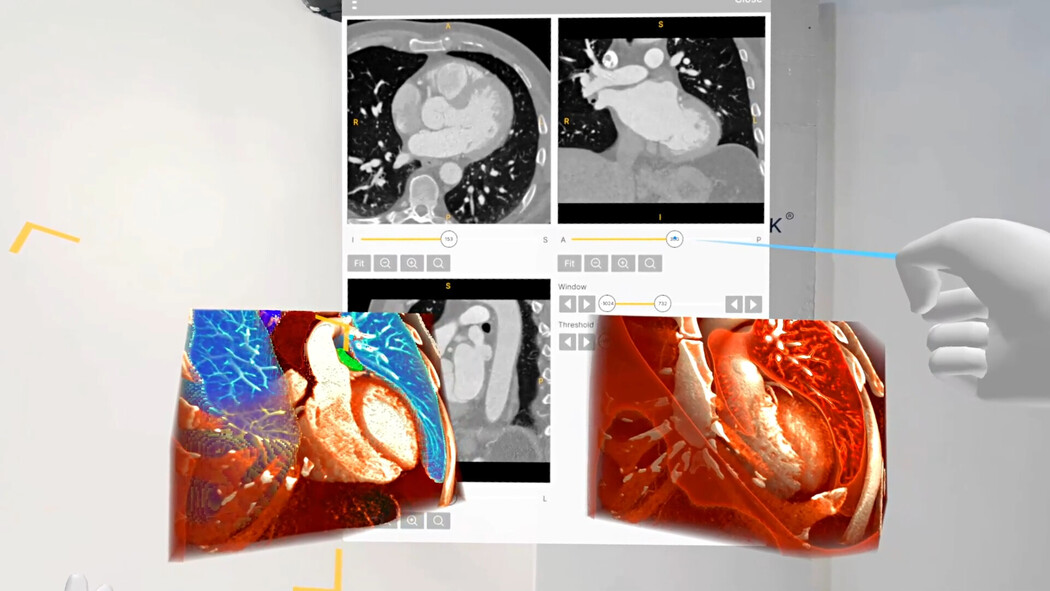
Pediatric residents were trained using models of healthy and congenitally diseased hearts presented both in VR and as 3D-printed replicas. Most preferred the VR format, as it allowed them to explore cardiac anatomy in different planes and orientations using an interactive slicing tool, providing a more detailed and intuitive learning experience.
Preoperative and interventional planning
VR allows cardiologists to plan and rehearse procedures like valve replacements and stent placements using interactive 3D models, simulating device deployment and access routes to reduce risks.
Accurate preprocedural planning is essential for transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). Virtual reality allows clinicians to import CT imaging data and create interactive 3D models of the aortic valve, surrounding anatomy, and access routes. Using VR, interventionalists can rotate, zoom, and manipulate the anatomy to better assess valve size, plaque distribution, and iliofemoral tortuosity.
Training and simulation
VR provides a safe platform for trainees to practice procedures such as catheterizations, electrophysiology interventions, or pacemaker implantations. By combining patient-specific 3D imaging with animated anatomical models, trainees can explore dynamic cardiac structures and device interactions, enhancing both anatomical understanding and procedural skills without putting patients at risk.
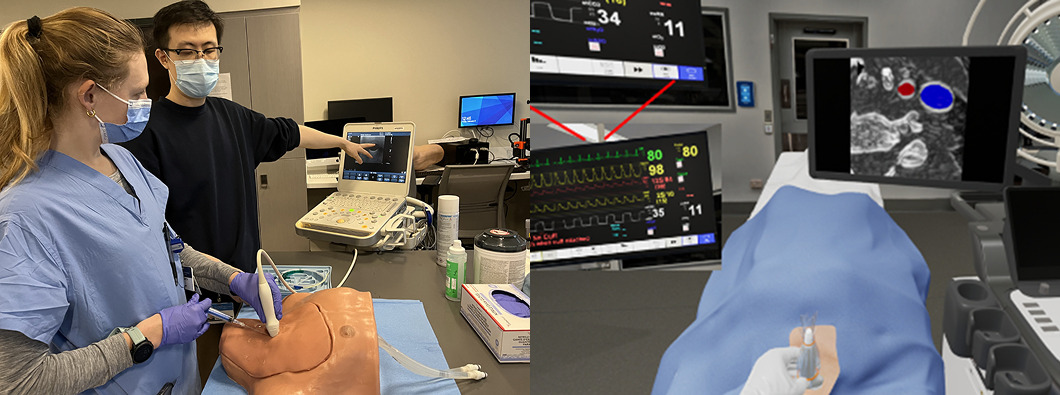
Standard manikin-based training and the simulator's operating room. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2024.07.002
Immersive simulation used in central venous catheter placement training served as a complementary tool for traditional mannequin-based learning, improving hand-eye coordination and overall trainee satisfaction. Similarly, VR-based methods for electrophysiology training allowed novice trainees to interact with dynamic cardiac anatomy, practice catheter manipulation, and develop accurate 3D mental models in a risk-free environment.
3D echocardiography
Echocardiographic images can be transformed into 3D dynamic models and analyzed within an immersive virtual reality environment to benefit cardiac education, procedural planning, and clinical understanding. When patient-specific echocardiographic data are integrated into an interactive 3D setting, clinicians gain a clearer perception of complex cardiac anatomy, crucial for all phases of care – from diagnosing paravalvular leaks or valve vegetations to guiding interventions that require precise spatial awareness, such as atrial septal defect closure.
Patient information
Patient information is about helping people understand their medical situation. With 3D imaging, doctors can turn complex scans into clear, easy-to-follow visuals of a patient’s body. This makes it easier to see what’s happening, understand the diagnosis, and explore treatment options. It also reduces anxiety by giving patients a sense of control through a clearer understanding of their condition.
Read more
How to get started
Medicalholodeck integrates with secure hospital systems, providing PACS access, HIPAA-compliant data handling, and full patient data security. It runs on stereoscopic 3D displays, VR headsets, mobile devices, and standard Windows systems, enabling flexible use in hospitals, classrooms, and training centers.
Specialized features for surgical planning are exclusive to Medical Imaging XR PRO. Currently, Medicalholodeck is available only for educational use. The platform is undergoing FDA and CE certification, and we expect Medical Imaging XR PRO to be available soon in the U.S. and EU markets.
For updates, regulatory news, availability, or questions contact info@medicalholodeck.com.